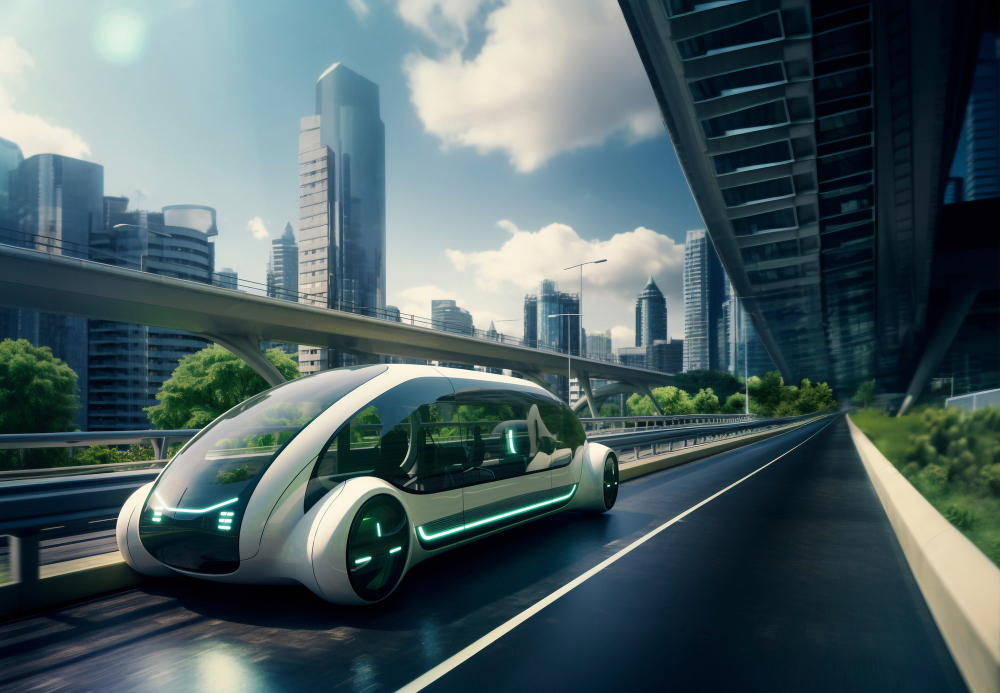
The transportation industry is on the brink of a revolutionary shift, one that promises to redefine how we think about mobility. Central to this transformation is the development of autonomous vehicles, which are set to change the way we drive, commute, and even plan our cities. At the heart of this evolution lies Artificial Intelligence (AI), which is playing an instrumental role in making autonomous vehicles a reality. By integrating advanced algorithms, machine learning, and sensor technologies, AI is enabling vehicles to navigate roads with minimal human intervention. As we look to the future, AI’s influence on autonomous vehicles is poised to reshape the entire transportation ecosystem, offering new levels of safety, efficiency, and convenience.
AI is transforming autonomous vehicles by enabling them to perceive and understand their surroundings. Traditional vehicles rely heavily on human drivers to process visual, auditory, and environmental cues. However, autonomous vehicles are equipped with a variety of sensors, including cameras, radar, and lidar, that collect vast amounts of data from the environment. AI algorithms then process this data in real time, allowing the vehicle to “see” and interpret its surroundings much like a human would, but with far greater accuracy and consistency. These AI systems analyze data to identify pedestrians, other vehicles, road signs, and obstacles, making split-second decisions to ensure the vehicle operates safely. By doing so, AI is creating vehicles that can drive themselves, reducing the likelihood of accidents caused by human error, such as distracted or impaired driving.
Moreover, the role of AI in autonomous vehicles extends beyond just sensing the environment. One of the most important functions of AI is decision-making. Autonomous vehicles must navigate complex roadways, respond to changing traffic conditions, and interact with other road users. This requires a highly sophisticated decision-making process, where AI algorithms evaluate multiple factors—such as speed, road conditions, and potential hazards—to determine the optimal course of action. Whether it’s slowing down to avoid an obstruction or changing lanes to avoid a collision, AI can make real-time decisions that are often faster and more precise than a human driver could. This capability ensures that autonomous vehicles can handle a wide range of driving scenarios with minimal risk, paving the way for safer roads and reduced traffic accidents.
As AI continues to evolve, it is also playing a significant role in improving the overall efficiency of autonomous vehicles. One of the major advantages of self-driving cars is their ability to optimize routes and manage traffic flow. AI-powered navigation systems can calculate the most efficient routes based on real-time data, including traffic congestion, road closures, and weather conditions. This can help reduce travel time, lower fuel consumption, and even decrease overall carbon emissions. In addition, AI can help coordinate autonomous vehicles within a larger fleet, allowing for more effective ride-sharing and reducing the number of vehicles on the road. This can lead to less traffic, improved air quality, and a more sustainable transportation system in the long run.
Looking at the future of autonomous vehicles, the integration of AI also has the potential to revolutionize public transportation. AI-enabled self-driving buses, trains, and other forms of mass transit could provide a more efficient and accessible alternative to traditional public transport. These autonomous vehicles could run on set routes, adjusting in real-time to traffic conditions, passenger demand, and other factors. AI systems could also help optimize the scheduling of these vehicles, ensuring that service is available when and where it’s needed most. By reducing the reliance on human drivers and increasing operational efficiency, AI-powered autonomous public transport could provide a more affordable and sustainable solution for urban areas, addressing issues such as overcrowding and limited access to transportation.
Of course, the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles powered by AI presents a number of challenges. One of the most significant hurdles is ensuring the safety and reliability of these systems. While AI has made tremendous strides in making self-driving cars safer, there is still a need for rigorous testing and validation to ensure that autonomous vehicles can handle every possible scenario on the road. Additionally, there are legal and regulatory concerns regarding liability in the event of an accident, as well as questions about how to integrate autonomous vehicles into existing transportation infrastructure. Governments and industry leaders must work together to develop comprehensive safety standards, legal frameworks, and regulatory policies that can guide the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles in a way that prioritizes public safety.
Furthermore, as AI systems become more integral to autonomous vehicles, there are concerns about cybersecurity. Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on software and cloud-based systems to process data, communicate with other vehicles, and make decisions. This makes them vulnerable to cyberattacks, which could have serious consequences for both the vehicle occupants and other road users. Ensuring the cybersecurity of these systems is a top priority for developers, who must implement robust security protocols and continuously monitor for potential threats. As AI evolves, it is crucial that autonomous vehicles are equipped with advanced security measures to prevent unauthorized access and protect against malicious interference.
The societal impact of AI in autonomous vehicles also cannot be overlooked. While these vehicles promise to improve road safety and transportation efficiency, they may also have far-reaching implications for employment and the economy. Autonomous vehicles could displace jobs in industries such as trucking, taxi services, and delivery. This shift could create new challenges in terms of workforce retraining and economic adaptation. It will be important for governments, businesses, and educational institutions to collaborate on programs that help workers transition to new roles within the AI-driven economy, ensuring that the benefits of autonomous vehicles are shared across society.
In terms of urban planning, AI-powered autonomous vehicles have the potential to transform cities. With fewer cars on the road, less need for parking spaces, and more efficient traffic management, cities could experience a significant reduction in congestion and pollution. Moreover, AI could help create smarter cities, where transportation systems are interconnected with other urban infrastructure, such as energy grids, waste management systems, and emergency services. This could lead to more efficient use of resources, better quality of life for residents, and a more sustainable urban environment.
Looking ahead, the role of AI in the future of autonomous vehicles is set to expand even further, with innovations in machine learning, sensor technology, and cloud computing continually enhancing the capabilities of self-driving cars. As these technologies mature, the vision of a fully autonomous, AI-powered transportation ecosystem may soon become a reality. By improving safety, efficiency, and sustainability, AI promises to not only revolutionize the way we travel but also to create a transportation system that is more accessible, equitable, and environmentally friendly. As the industry progresses, it will be exciting to see how AI continues to shape the future of autonomous vehicles and the broader transportation landscape.